
[ Archive ]

 |
CIMSS-NOAA Weekly Report
[ Archive ] |
 |
IN THE PRESS:
ITEMS FOR THE ADMINISTRATOR:
ITEMS FOR THE ASSISTANT ADMINISTRATOR:
ITEMS FOR THE OFFICE DIRECTOR, ORA:
Teacher Workshop on Satellite Meteorology: The Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies (CIMSS), in collaboration with the Wisconsin Space Grant Consortium, held a 2-day teacher workshop on Satellite Meteorology for Grades 7-12. Sixteen teachers attended the workshop which included presentations on operational and research satellites, and hands-on activities using a CIMSS designed CD on satellite meteorology. The teachers provided feedback on the design of the CD and how they would use the material in their classes. Six teachers gave an overall evaluation of "very good" and the remaining nine gave an evaluation of "excellent." The CIMSS team is now reviewing their suggestions for incorporation in the next version of the CD. (S. Ackerman, CIMSS, 608-263-3647)
ITEMS FOR THE DIVISION CHIEF, ARAD:
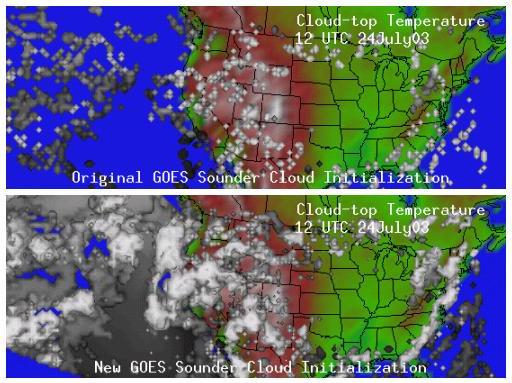 (Click on image to enlarge)
(Click on image to enlarge)Reduction in Latency of GOES WF_ABBA Fire
Product: In response to a request from the hazards community
and fire weather forecasters (P. Bothwell, Storm Prediction Center),
the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) Wildfire
Automated Biomass Burning Algorithm (WF_ABBA) processing system was
modified to reduce the latency. GOES-12 WF_ABBA fire product
ASCII files are now available via anonymous ftp at the Cooperative
Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies (CIMSS) within 20-25
minutes of the GOES-12 image time. The alpha-blended composite
fire imagery are available on the web (http://cimss.ssec.wisc.edu/goes/burn/wfabba.html)
within approximately 30 minutes. CIMSS hopes to decrease the
latency even further by implementing the WF_ABBA on new hardware in the
next few months. (C.
Schmidt, CIMSS, 608-262-7973, E. Prins, E/RA2, 530-271-2256)
Ice Surface Temperature Paper Submitted to
Scientific Journal: A paper titled "Sea ice surface temperature
product from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS)"
was submitted to the journal IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and
Remote Sensing. The authors are D. Hall (NASA Goddard Space
Flight Center (GSFC)), J. Key, K.A. Casey (GSFC), G.A. Riggs (GSFC),
and D.J. Cavalieri (GSFC). The paper introduces the MODIS sea ice
temperature product, the retrieval methodology, and validation over the
Arctic and Antarctic.
(J. Key, E/RA2,
608-263-2605)
First Step in Polar Winds Transition to Operations Underway: The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) polar winds product is generated in real-time at the Cooperative Instititue for Meteorological Satellite Studies (CIMSS). The first step in the process of transitioning the product to NESDIS operations is to transfer the software to the Forecast Products Development Team (FPDT) so that FPDT can run the code run in parallel with CIMSS. Though the transition to NESDIS operations is not scheduled until fiscal year 2005, this first step is underway. Software differences at CIMSS and FPDT have been identified and test cases have been run. (J. Key, E/RA2, 608-263-2605, D. Santek, CIMSS, 608-263-7410, C. Velden, CIMSS, 608-262-9168, J. Daniels, E/RA2, 301-763-8204)
Abstracts on GOES-R Submitted for AMS Annual
Meeting: Three abstracts were submitted for the upcoming annual
American Meteorological Society (AMS) meeting on the topics of the
Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI), Hyperspectral Environmental Suite (HES)
and HES modeling. The titles are: Study of the Advanced Baseline
Imager (ABI) on the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite
(GOES) -R and beyond, Study of the Hyperspectral Environmental
Suite (HES) on the GOES-R and beyond and HES Simulation Study
using Cube Data from MM5. The authors include: Jun Li,
Fengying Sun, Mat M. Gunshor, Chris C. Schmidt, W. Paul
Menzel, James Gurka, Justin Sieglaff, Derek Posselt and Timothy,
J. Schmit.
(T. Schmit, E/RA2,
608-263-0291, J. Li, CIMSS,
608-262-3755, F. Sun, CIMSS, 608-262-7889)
VISITORS:
CREST Visitors: Keven McCann and Ray Rogers, collaborators from the University of Maryland-Baltimore County (UMBC) and part of the Cooperative Remote Sensing Science and Technology (CREST) Center, visited CIMSS for two days. After discussions on cloud detection and cloud property estimation, it was agreed to pursue some special case studies from the Aqua overpasses between June 1 through July 8 2003. Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies (CIMSS) scientists will collect and provide products from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS); UMBC/CREST scientists will collate the satellite and surface datasets and select interesting case study days for further investigation. This work will try to determine the MODIS threshold for detection of thin cirrus (how thin is detected), reinforce algorithm adjustments to improve MODIS detection of boundary layer marine stratus clouds, validate MODIS cloud overlap detection, corroborate MODIS cloud phase estimation, validate MODIS cloud top pressure estimates, and investigate the influence of TPW on cloud detection. (S. Ackerman, CIMSS, 608-263-3647)
NEXT WEEK: