
[ Archive ]

 |
ASPB and CIMSS Weekly Report
[ Archive ] |
 |
IN THE PRESS:
ITEMS FOR THE ADMINISTRATOR:
ITEMS FOR THE ASSISTANT ADMINISTRATOR:
ITEMS FOR THE OFFICE DIRECTOR, STAR:
ITEMS FOR THE DIVISION CHIEF, CoRP:
Radiative effects of Asian Wildfires during April 2008: A poster entitled “Radiative effects due to tropospheric ozone and carbonaceous aerosol enhancements caused by Asian wildfires during Spring, 2008" was presented at the American Geophysical Union Fall meeting 12-17 December, San Francisco, CA. The poster describes results from collaborative studies by the Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies (CIMSS) and the NASA Langley Research Center using the Real-time Air Quality Modeling System (RAQMS) simulations and Langley Fu-Liou radiative transfer model to evaluate the radiative forcing due to emissions from fires in Kazakhstan, Siberia, and Thailand during April 2008. Differences between the RAQMS simulations with observed fires and no Asian fire emissions are used to determine the perturbations due to Asian wildfires. The predominant effect at the surface is negative forcing. The largest is of the order of -30 to -60 W/m2 near the fire zone. The calculated results depend significantly on the predicted cloudiness as well as the vertical distribution of black and organic carbon aerosols (R.B. Pierce, E/RA2, 608-890-1892, brad.pierce@noaa.gov)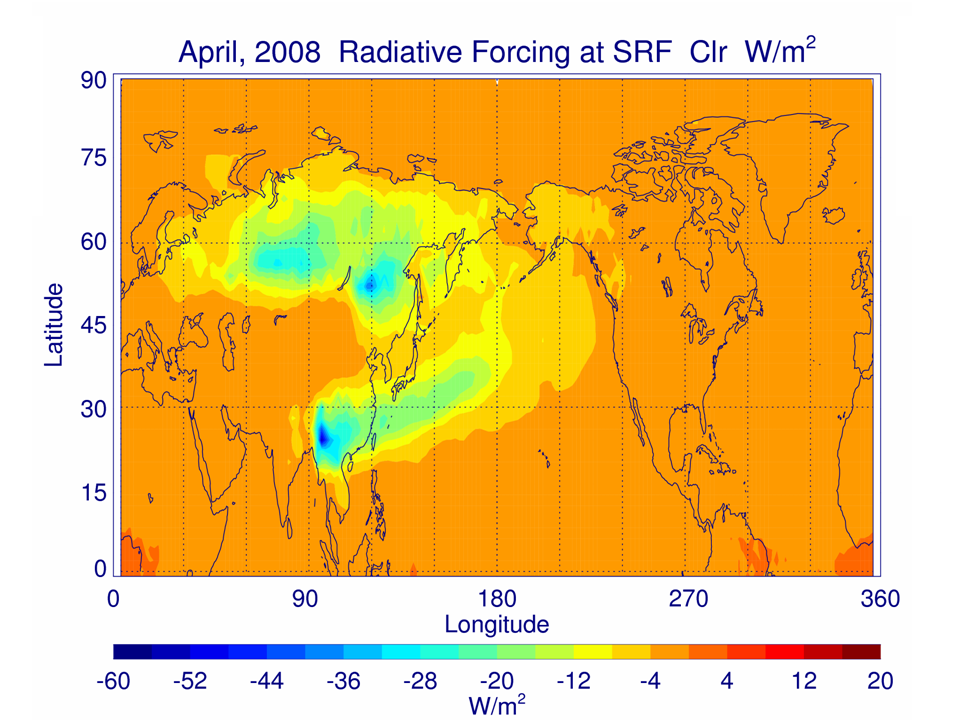 (Click image to enlarge)
(Click image to enlarge)
VISITORS:
NEXT WEEK:
LOOKING AHEAD:
| Archived Weeklies Page | Submit a report item |