
[ Archive ]

 |
ASPB and CIMSS Weekly Report
[ Archive ] |
 |
IN THE PRESS:
ITEMS FOR THE ADMINISTRATOR:
ITEMS FOR THE ASSISTANT ADMINISTRATOR:
ITEMS FOR THE OFFICE DIRECTOR, STAR:
GOES Satellite Support for NASA HS3 Missions: The
Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies (CIMSS) is
providing real-time mission and hazard-avoidance support for the Global
Hawk drones flying in the Hurricane and Severe Storm Sentinel (HS3)
field experiment, operating out of Wallops Island, Virginia. HS3
missions start on August 20, and continue through September 24, and will
investigate and overfly Atlantic hurricanes with both high-altitude
dropsondes and remote sensing instruments. One of these instruments is
the Scanning HIS, developed at the University of Wisconsin Space Science
and Engineering Center (UW-SSEC). This year, CIMSS will provide
critical decision-making products derived from GOES, including cloud-top
heights (CTH) and tropical overshooting tops (TOTs). Both of these
products are being developed and demonstrated as part of the NOAA/NESDIS
GOES-R Risk Reduction and Proving Ground programs. This week, the
Global Hawks ferried from Dryden Air Force Base in California, to
Wallops Island (see accompanying animation). In addition, the GOES-14
special 1-minute rapid scanning operations will coincide with the first
10 days of HS3, and will also benefit mission support when activated
over targeted hurricanes. (S. Monette, CIMSS, 608-262-0968; C. Velden,
CIMSS, 608-262-9168)
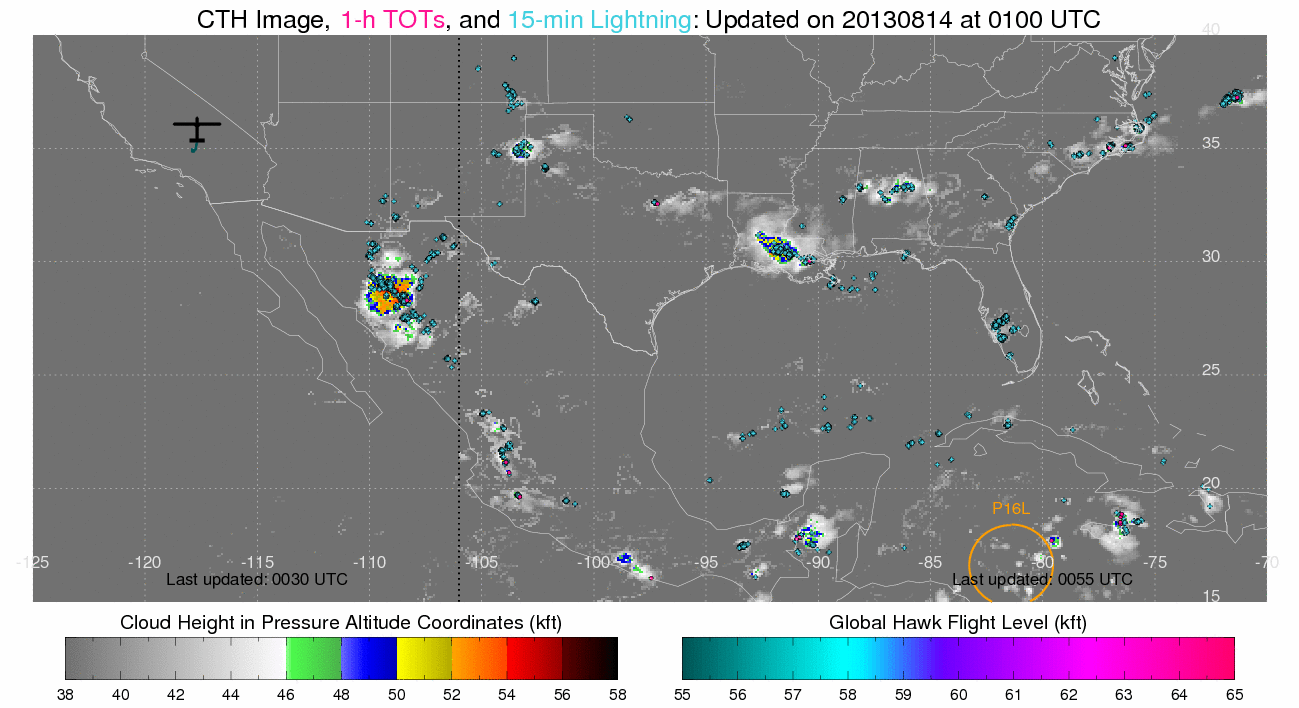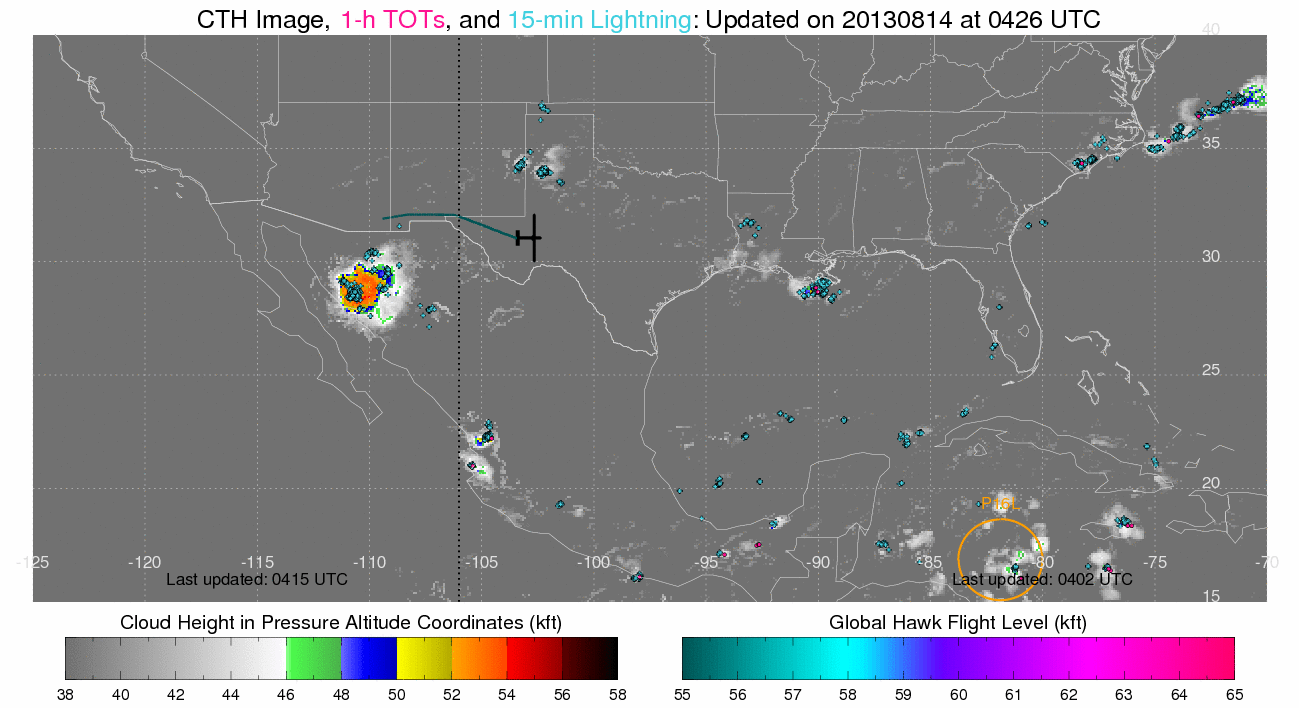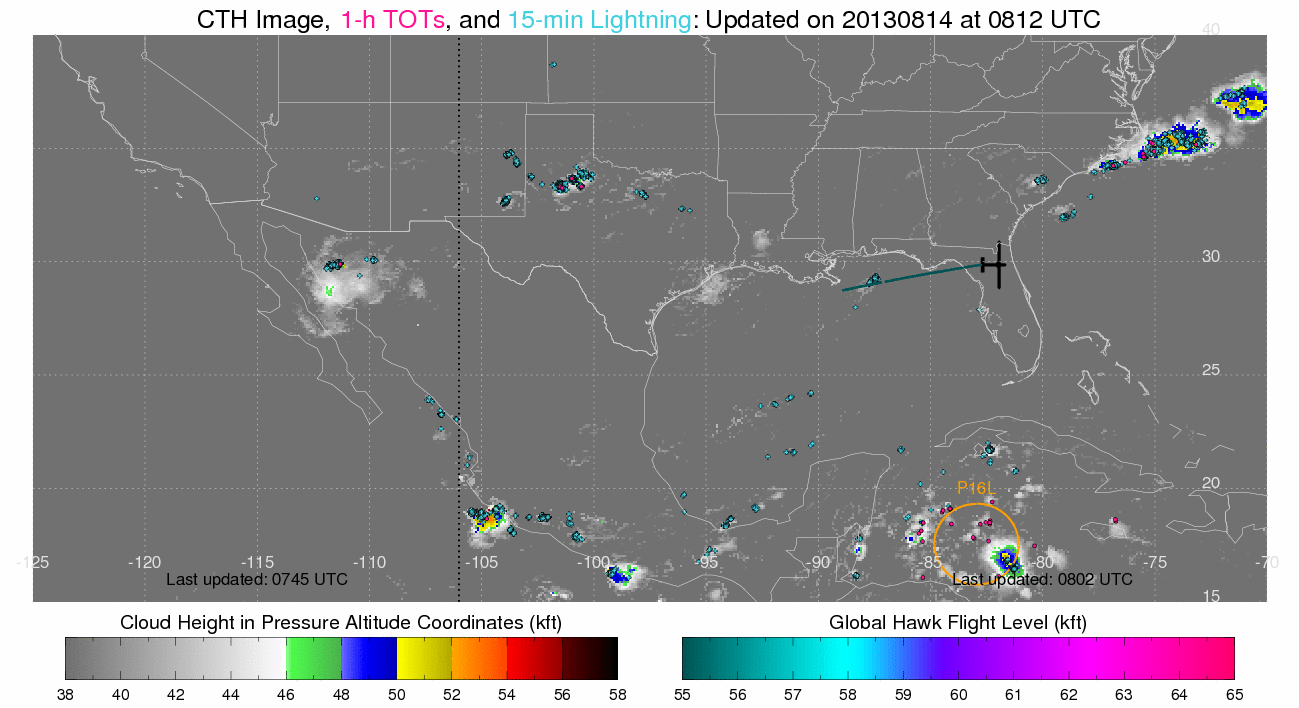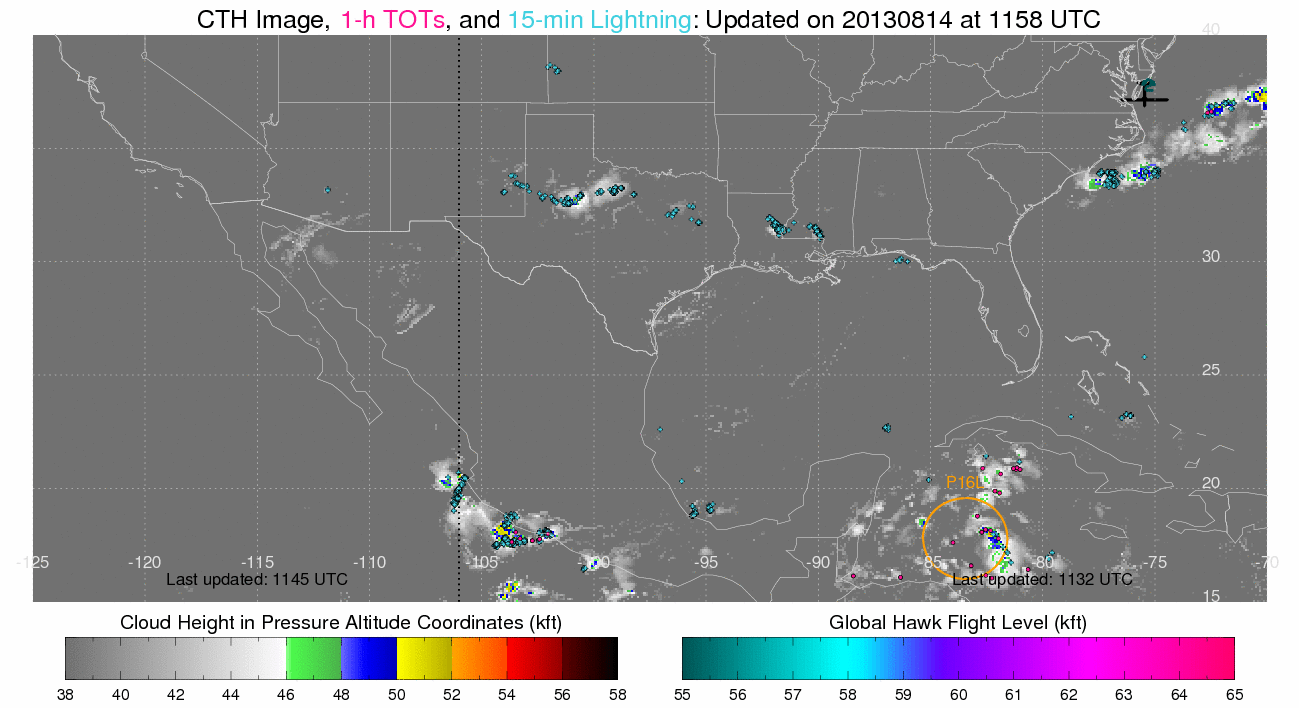 (Click image to enlarge)
(Click image to enlarge)
Figure caption: Cloud top height (CTH), tropical overshooting tops, and
lightning while the Global Hawks ferried from Dryden Air Force Base in
California, to Wallops Island.
GOES-12 Retires After More Than 10 years of Service: Geostationary
Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES)-12 acquired its last sounder
images on August 13 and last imager image on August 15. GOES-12 was
launched on July 23, 2001, and GOES-12 transmitted data from 16 August
2001 – 7 January 2002, and then more or less continuously from January
16, 2003 onward. GOES-12 initially served as GOES-East, replacing
GOES-8. After April, 2010, when GOES-13 began service as GOES-East,
GOES-12 was moved to 60 West longitude and supplied data over South
America. To mitigate the loss of GOES-12, two new image sectors over
South America were added by NOAA NESDIS to the GOES-East rapid scan
schedule
(http://cimss.ssec.wisc.edu/goes/blog/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/2MIN_SA_a_b_zoom.gif).
More information at
http://cimss.ssec.wisc.edu/goes/blog/archives/13650. (T. Schmit, E/RA2,
608-263-0291, tim.j.schmit@noaa.gov; S. Lindstrom, CIMSS, 608-263-4425;
J. Nelson, CIMSS, 608-263-6013, jim.nelson@ssec.wisc.edu)
(Click image to enlarge)
Figure caption: The five spectral bands of the GOES-12 Imager of the last Imager image on 15 August 2013.
ITEMS FOR THE DIVISION CHIEF, CoRP:
New Book Published: A new book entitled "Climate Science for Serving Society: Research, Modeling and Prediction Priorities" has been published by Springer. Jim Kossin (NOAA/NESDIS/NCDC) served as an author on the peer-reviewed chapter "Challenges in estimating and understanding recent changes in the frequency and intensity of extreme climate and weather events." The full citation and the chapter PDF are available at http://www.ssec.wisc.edu/~kossin/pubs.html. (J. Kossin, NCDC, 608-265-5356)
Special GOES-14 Imager Rapid-scan Imagery: The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES)-14 satellite was placed into Super Rapid Scan Operations for GOES-R (SRSOR) for three days. Image loops of pyrocumulonimbus (http://cimss.ssec.wisc.edu/goes/blog/archives/13649), fog (http://cimss.ssec.wisc.edu/goes/blog/archives/13684) and convection (http://cimss.ssec.wisc.edu/goes/blog/archives/13697) were monitored. In this updated SRSOR mode, experimental rapid scan images are no longer interrupted by full disk images. (T. Schmit, E/RA2, 608-263-0291, tim.j.schmit@noaa.gov; S. Bachmeier, CIMSS, 608-263-3958; J. Gerth, CIMSS; J. Robaidek, SSEC, 608-262-6025, jerrold.robaidek@ssec.wisc.edu)
Manuscript on smoke impacts on tornado severity submitted to Science: A manuscript entitled “Central American biomass burning smoke can increase tornado severity in the US” by P. E. Saide, S. N. Spak, R. B. Pierce, J. A. Otkin, T. Schaack, A. Heidinger, A. M. da Silva, M. Kacenelenbogen, J. Redemann and G. R. Carmichael was submitted to Science. The manuscript uses coupled aerosol and meteorological forecasts and observations of the 27 April 2011 historical tornado outbreak to show that adding smoke to an environment already conducive to severe thunderstorm development can increase the likelihood of significant tornado occurrence. The results of this study suggest that inclusion of aerosols in severe weather forecast models will likely help improve the predictability of these extreme events, which can improve the timeliness and accuracy of severe weather alerts within future operational forecast systems. (R.B. Pierce, E/RA2, 608-890-1892, brad.pierce@noaa.gov)
VISITORS:
GOES-R Program Office Visitor: Robert Iacovazzi, from the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES)-R Program Office (GPO) visited on 16 August 2013. Many topics were discussed relating to GOES-R calibration / validation activities. (T. Schmit, E/RA2, 608-263-0291, tim.j.schmit@noaa.gov)
NEXT WEEK:
LOOKING AHEAD:
| Archived Weeklies Page | Submit a report item |