In the Arctic cloud cover is extensive at all times of the year, with monthly means ranging from 50-80%. Retrievals of the clear sky surface broadband albedo are therefore of limited utility for climate studies. Is it possible to estimate the surface albedo under cloud cover from visible satellite data?
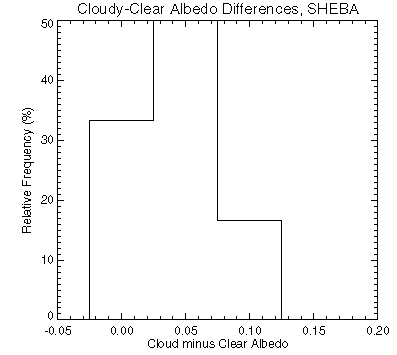
The differences between cloudy and clear albedos from surface measurements made during the SHEBA experiment are shown in the figure below. Overall, the cloudy sky albedo is higher than the clear sky albedo by about 0.05 (5% absolute), though it ranges from slightly less than zero (probably data error) to more than 0.1. Clouds do not absorb significantly in the visible portion of the spectrum but do absorb well in the near-infrared. Snow and ice are good reflectors of visible radiation but poor reflectors in the near-infrared. Therefore, clouds tend to increase the proportion of radiation in that portion of the spectrum where snow/ice reflect most (the visible), so the broadband albedo increases under cloud cover.
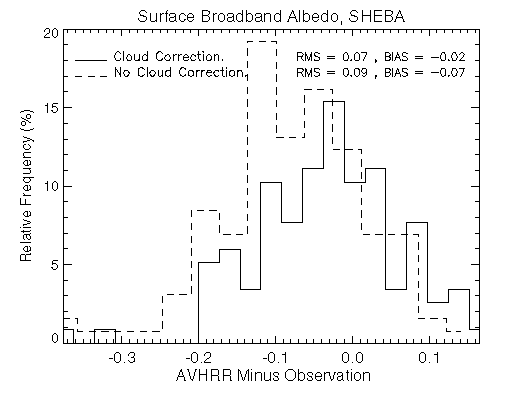
The procedure was applied to the SHEBA area and time period. Results are shown below for retrievals with and without the cloudy sky adjustment, as compared to surface measurements. The improvement in the retrieved albedo is significant.
Key, J., 2000. The Cloud and Surface Parameter Retrieval (CASPR) System for Polar AVHRR Data User's Guide. Space Science and Engineering Center, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, 62 pp.
Stroeve, J., J. Box, C. Fowler, T. Haran, J. Key, and J. Maslanik, 2000. Intercomparison between in situ and AVHRR Polar Pathfinder-derived surface albedo over Greenland. Rem. Sens. Environ., submitted (April 2000).
Key, J., X. Wang, J. Stroeve, C. Fowler, 2000. Estimating the cloudy sky albedo of sea ice and snow from space. J. Geophys. Res., 106(D12), 12489-12497.
DeAbreu, R.A., J. Key, J.A. Maslanik, M.C. Serreze, and E.F. LeDrew, 1994. Comparison of in situ and AVHRR-derived surface broadband albedo over Arctic sea ice. Arctic, 47(3), 288-297.