 |
CIMSS-NOAA Weekly Report
[ Archive ] |
 |
ASPB AND CIMSS WEEKLY HIGHLIGHTS FOR THE WEEK ENDING SEPTEMBER 15, 2006
IN
THE PRESS:
ITEMS
FOR THE ADMINISTRATOR:
ITEMS FOR THE ASSISTANT ADMINISTRATOR
ITEMS FOR THE OFFICE DIRECTOR, STAR:
Texas Air Quality Study Field Campaign:
Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies (CIMSS)
scientist Chris Schmidt, with support provided by STAR's air quality
program, participated in the 2006 Texas Air Quality Study (TEXAQS)
based in Houston, Texas. Using multiple platforms such as ground,
aircraft, ship, and satellites, this NOAA field campaign is being
carried out to study air quality issues in the southern United
States. Mr. Schmidt was at the field campaign site
from August 29 through September 7, 2006 providing support to
the field campaign by interpreting satellite data that aid in
aircraft/ship deployment. Near real time satellite data products
that were provided to the field campaign included imagery of GOES fire
hot spots, fire emissions, aerosol optical depths, and surface
ultraviolet fluxes. STAR scientists in collaboration with
University of Wisconsin scientists will conduct post mission analysis
of satellite and ground observations to understand atmospheric
processes impacting regional air quality in the southern United
States. (C. Schmidt, CIMSS,
608-262-7973; S. Kondragunta, E/RA2)
First Meeting of NOAA International Affairs Council Polar Committee:
The newly-formed Polar Committee of the NOAA International Affairs
Council (IAC) held its first formal meeting on September 7. The
committee was established to serve as a policy coordinating forum, to
maintain awareness of NOAA’s work in the polar regions and, as
appropriate, to address crosscutting program issues including review
and oversight for PPBES purposes. Jeff Key is the NESDIS representative
on the IAC Polar Committee, which is led by Pam Toschik (NOAA Office of
International Affairs). The NESDIS representative on the IAC is
Brent Smith (NESDIS International and Interagency Affairs Office).
Eric Madsen participates as a NESDIS International and Interagency Affairs Office liaison to the Polar Committee.
Recent activities of the committee include reviewing the FY09 Strategic
Portfolio Analyses, commenting on a proposal by Norway to change the structure of the Arctic Council working groups, and preparing for Senate briefings on NOAA's plans for the International Polar Year (IPY). (J. Key, E/RA2,
608-263-2605, jeff.key@noaa.gov)
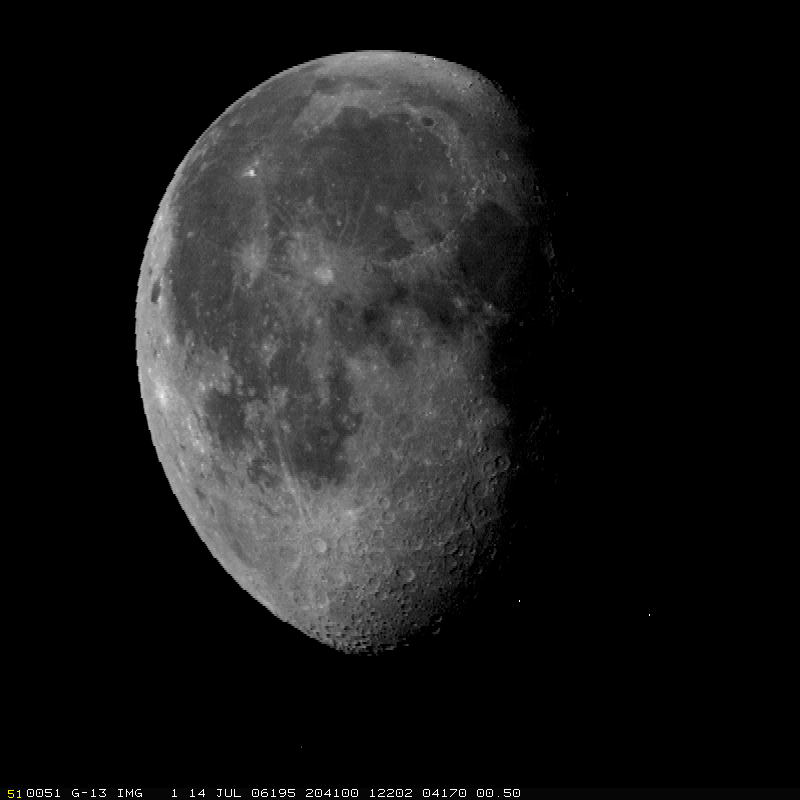
GOES-13 Images of the Moon:
In conjunction with the Space Science and Engineering Center (SSEC)
Data Center, the Advanced Satellite Products Branch (ASPB) supplied Man
computer Interactive Data Access System (McIDAS) images of several
periods when the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite
(GOES)-13 imager scanned the moon. The visible and near-infrared band
data were supplied to X. Wu, of Satellite Applications and Research
(STAR) for investigating the usefulness for calibration of using images
of the moon. Due to the importance of GOES lunar calibration for GOES
operations and possibly GOES-R, special test was designed and executed
during GOES-13 Post Launch Test. (T. Schmit, E/RA2,
608-263-0291, tim.j.schmit@noaa.gov)
 (Click image to enlarge)
(Click image to enlarge)
Figure caption: Sample visible image of the moon from GOES-13 imager taken during the Post Launch Test.
ITEMS FOR THE DIVISION CHIEF, CoRP
GOES-R Instrument Issues Meeting:
T. Schmit presented, along with J. Li (CIMSS), a talk entitled
"Advanced Baseline Imager (ABI) versus Sounder Trade Study " at the
Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES)-R Instrument
Issues meeting on September 13 in Silver Spring, MD. The meeting
was hosted by the Algorithm Working Group (AWG) and the GOES
Program Office. Many others from Advanced Satellite Products Branch
(ASPB) and Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies
(CIMSS) also teleconferenced to this meeting. (T. Schmit, E/RA2,
608-263-0291, tim.j.schmit@noaa.gov)
Manuscript on Cloud Top Heights Accepted:
A paper entitled " Comparison of MISR and MODIS cloud-top heights in
the presence of cloud overlap" was accepted for publication in Remote Sensing of Environment.
The paper by C. Naud (Columbia University), B. Baum (Space Science and
Engineering Center, SSEC), M. Pavolonis, A. Heidinger, R. Frey
(Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies, CIMSS),
and H. Zhang (CIMSS) presents an analysis on the performance of the
Multiangle Imaging Spectroradiometer (MISR) and the Moderate Resolution
Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) cloud top height algorithms when
multi-layered clouds are present. (M. Pavolonis, E/RA2, 608-263-9597,
Mike.Pavolonis@noaa.gov, A. Heidinger, E/RA2, 608-263-6757)
Investigating Stray-Light Effects During GOES-13 Eclipse:
Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES)-13 is going
through a series of engineering checks as it continues to be checked
out by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The unique
spacecraft design of GOES-13 allows it to collect data through solar
eclipse periods (when the sun is behind the Earth) and thus scientists
are seeing data during periods where no data was collected on previous
GOES satellites. This resulted in a unique opportunity to view
data which has been contaminated by direct solar radiation.
Researchers at the Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite
Studies (CIMSS) investigated the effects of direct solar contamination
on the bands of the GOES-13 Imager to help NOAA determine which data
can be disseminated to users and determined that all five bands of the
Imager are corrupted by solar intrusion; the geographical extent of the
intrusion must still be determined so that NOAA can determine if
partial scans during these time periods can still be used. (M.
Gunshor, CIMSS,
608-263-1146; T. Schmit, E/RA2, 608-263-0291, tim.j.schmit@noaa.gov)
 (Click image to enlarge)
(Click image to enlarge)
Figure caption: Geostationary Operational
Environmental Satellite (GOES)-13 Imager nighttime visible image
showing the sun's radiation (top panel). GOES-13 13.3 um band
time difference image showing the effect of the sun (lower
panel). The few bad horizontal lines are due to the satellite
data ingest.
Severe Convection Viewed from Four GOES Satellites:
Severe convection developed in eastern portions of the Texas panhandle
region on September 10, 2006, producing wind gusts to 67 miles per
hour, golf-ball size hail, and flash flooding in parts of Cottle
county. A 16-panel image shows visible and InfraRed (IR) channel
data from all four of the currently operating Geostationary Operational
Environmental Satellites (GOES-10, GOES-11, GOES-12, and GOES-13) at
the time of the severe weather reports. In addition, an animation of
GOES-10 Super Rapid Scan Operations (SRSO) visible images at
1-minute intervals is available on the Cooperative Institute for
Meteorological Satellite Studies (CIMSS) Satellite Blog at http://cimss.ssec.wisc.edu/goes/blog/category/goes-10/.
(S. Bachmeier, CIMSS, 608-263-3958)
 (Click image to enlarge)
(Click image to enlarge)
Figure caption: GOES-10, GOES-11, GOES-12, and GOES-13 visible and IR
channel images of severe convection over Cottle county, Texas on
September 10, 2006.
Manuscript Review: M. Pavolonis completed a manuscript review for the Journal of Geophysical Research.
The manuscript deals with multi-layered cloud property retrievals. (M.
Pavolonis, E/RA2, 608-263-9597, Mike.Pavolonis@noaa.gov)
Other Meetings and Telecons:
(None)
VISITORS:
NEXT WEEK:
LOOKING AHEAD:
Archived Weeklies Page




 (Click image to enlarge)
(Click image to enlarge)